
|
Архитектура Аудит Военная наука Иностранные языки Медицина Металлургия Метрология Образование Политология Производство Психология Стандартизация Технологии |

|
Архитектура Аудит Военная наука Иностранные языки Медицина Металлургия Метрология Образование Политология Производство Психология Стандартизация Технологии |
Activity 6. Insert prepositions
1. Because such publications do not conform ___ any standardized rules, this information is not computer readable. 2. It must be terrible to be subject ___ cyberbullying. 3. We never thought him to be prone ___ suicide. 4. She went to the shop where she was diddled ___ ___ £15 when buying a pair of flip-flops. 5. He regarded it as an infringement ___ his privacy. 6. I would not imagine him acting ___breach of law. 7. The companies would have to comply ___ the new safety standards and procedures. Activity 7. State the type of logical relations between the following concepts:
Activity 8. Decode a Jewish proverb about crime and comment on it:
http://puzzlemaker.discoveryeducation.com/cryptogramSetupForm.asp Activity 9. Explain the difference between the following concepts using the Venn diagram below:
Activity 10. Name at least 2 kinds of crime that involve: 1. violation of social norms 2. telephone calls 3. copyright violations 4. misdirecting or impeding traffic 5. stealing confidential data 6. identity theft Activity 11. Arrange the computer crimes in the ascending order of the difficulty of committing them. Activity 12. What kind of crime you might be a victim to if: 1. Your telephone/Internet bills have risen significantly. 2. Your account information has changed. 3. You receive threats and insults on the net. 4. The money in your bank account has disappeared. 5. You receive a lot of unwanted e-mails. 6. Your copyright is violated. 7. You can’t leave an Internet page.
Activity 13. Describe an instance of your suffering from an Internet crime. Activity 14.What could you do not to fall prey to Internet criminals (name at least 3 measures). Activity 15. Do a mini-research and add to the above list more recent types of computer crime. TEST
Module 8. CYBER SECURITY
Usage | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | Attack (n) | an attempt to gain unauthorized access to system services, resources, or information, or to compromise system integrity | a(n) violent/aggressive/active/passive/ inside/outside/spoofing ~; come under ~; be open to/ launch an ~; syn. penetration, intrusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Authenticate (v) | prove or show sth to be true, genuine, or valid; confirm the correctness of the claimed identity | ~ a document/identity; authentication (n): certificate-based/biometric ~; authenticity (n); syn. verify, validate, confirm Cf. authorize | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | Authorize (v) | grant a right or a permission to a system entity to access a system resource | ~ sb to do sth; be ~ed to do sth; authorization (n): obtain/sign/present ~; authorized (adj): an ~ payment/dealer; authority (n): have/exercise ~ over sth/sb; delegate ~ to sb; syn. entitle Cf. authenticate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Back door (adj) | a feature or a defect of a computer system that allows secret unauthorized access to data | leave/activate a ~ to a computer; open a ~ to hackers; syn. trap door
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | Certificate (n) | an official document recognizing sb as possessing certain qualifications or meeting certain standards | issue/renew/revoke/ grant/get/obtain a ~; ~ renewal/revocation; certify (v); certified (adj): a ~ CISCO programmer/accountant/ instructor; certification (n): ~ authority/procedure syn. accredit, qualify | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | Cipher (n) | sth written in a code; a cryptographic algorithm | ~ text/mode/key; write sth in ~; (de)cipher (v), (de)ciphered (adj): a ~ message syn. code, encrypt | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | Classified (adj) | sth or sb arranged in categories according to shared qualities or characteristics; sth categorized as officially secret, access to which requires authorization | a ~ document/information/ advertisement; be ~ according to into some categories; classify (v): ~ sb/sth into … according to…; classification (n): ~ level/type/category; syn. categorize ant. declassified, unclassified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | Code (n) | a system of symbols used to represent information in the form other than the original one | write/crack a ~; ~ string/generator/ inspection/length/point; source/malicious/machine/ASCII ~; decode (v), encode (v); syn. cipher, cryptogram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | Compromise (v) | reach an agreement or settlement of a dispute by each side making concessions; cause to become vulnerable or function less effectively | ~ a system/data/security/one’s principles; ~ on sth; compromise (n): reach a ~; (un)compromised (adj); syn. undermine, weaken, concession | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | Confidential (adj) | information to be disclosed only to those authorized to view it | ~ information/service/details/ performance check; keep sth ~; on a ~ basis; divulge ~ information; confidentiality (n): ~ agreement, breach of ~, total ~, under the terms of ~, guarantee/request ~; confidentially (adv); syn. private, personal, secret, sensitive, classified ant. open, public | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | Corruption (n) | dishonest or fraudulent conduct by those in power, typically involving bribery; degradation of a computer database or program by alteration or the introduction of errors | expose/root out ~; allegation of ~; prevent accidental data ~; lead to/cause data ~; rotten with ~; corrupt/ed (adj); ant. integrity Cf. bribery | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | Dedicated (adj) | devoted to a task or purpose; exclusively allocated to or intended for a particular purpose; a mode of IS operation, wherein all users are authorized to access all data handled by the system | be ~ to a career/cause/team; a ~ channel/security mode/link/ terminal/web page/graphics/card/ employee/LAN /line; dedicate (v): ~ oneself to sth/sb; ~ sth to sb; dedication (n); syn: committed, exclusive, allocated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | Deny (v) | refuse to give sth requested or desired to sb; refuse to admit the truth or existence of sth | ~ access/the existence of sth/evidence/a law/a privilege/a claim; ~ sb the right to sth; ~ oneself the pleasure of sth/doing sth; ~ that…; denial (n): ~ of service/access;(un)deniable (adj);syn: reject, decline | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | Encrypt (v) | convert (information or data) into a code, especially to prevent unauthorized access | ~ information/data/a password/a message; cryptography (n), (un)encrypted (adj);encryption (n): ~ standards/code; syn. code, cypher ant. decrypt, decode | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | Expire (v) | (of a document, authorization, or agreement) reach the end of the validity period | license/contract/term/authorization ~s on/ at …; expiry (n): ~ date; upon/before/after ~; best before ~; expiration (n), expired (adj) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | Expose (v) | make sth visible by uncovering it; release sensitive data to an unauthorized entity (as a result of theft, wiretapping, etc.), cause someone to be vulnerable or at risk | ~ sb to danger/risk/treatment/injury; ~ the nature/flaw/defect of sth; exposed (adj): ~ to culture/best practices; ~ and vulnerable; exposure (n): deliberate/unintentional ~; syn. endanger, imperil, jeopardize sb/sth; familiarize/acquaint sb with sth | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | Detect (v) | discover or identify the presence or existence of sth | ~ (a/n) intrusion/virus/attempt/cancer /crime/changes/trend; detector (n): fire ~; detective (n); syn. become aware/conscious of, perceive | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | Digital (adj) | relating to, using, or storing data or information in the form of signals expressed as series of the digits 0 and 1 | ~ certificate/signal/age/map/assistant/ TV/generation/technology/revolution/ recording/cassette/copier/image; digitize (v); digit (n); syn. computerized ant. analogue | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | Disrupt (v) | interrupt or prevent the correct operation of system services and functions | ~ the workflow/operations/activities/ a(n) application/mechanism/process/ system/production/plans; disruption (n), disruptive (adj); syn. discontinue, interfere | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | Fail (v) | be unsuccessful in achieving one’s goal; cease to work properly; break down | ~ to qualify/to meet the standards/to do sth; ~ in one’s attempt to do sth /an exam; a ~-safe mode; a ~ grade; ~; failure (n): ~ control; control ~; be doomed to ~; syn. breakdown, malfunction, go wrong; ant. succeed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 | Filter (n) | a piece of software that processes data before passing it to another application, for example by reformatting characters or removing unwanted types of material | ~ out/through sth; ~ a system/a message/traffic/ information/calls; filter (n): water/oil/software/removable ~; install a ~; ~ capability syn. sift, purify | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | Firewall (n) | either a hardware program or a feature intended to filter incoming and outbound traffic | install/construct/bypass a ~; monitor computers and networks through a ~; invest in a software ~; up-to-date/outdated/personal ~; voice ~; syn: security, gateway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | Identity (n) | the characteristics determining who or what a person or thing is | ~ card; personal/mistaken/group/corporate/ racial/social/ethnic/national ~; identify (v): ~ sb (oneself) with sth/sb; identifier (n); identification (n); syn. selfhood | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | Integrity (n) | the quality of being honest and having strong moral principles; the state of being undivided; internal consistency or lack of corruption in electronic data | a man of ~; data/database ~ check; check sth for ~; structural/moral/territorial ~; ensure/preserve ~; integral (adj), (dis)integrated (adj); syn. soundness, wholeness, solidity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 | Intrude (v) | enter with a disruptive or adverse effect;gain access to sensitive data without authorization by circumventing a system's security protection | ~ on sb’s privacy/into sb’s private life; intruder (n), intrusion (n): defend sth against ~; syn. encroach, infringe on, invade, disrupt Cf: trespassing, penetration, reverse engineering | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | Log in/on (v) | gain access to a session to use system resources usually by providing a user name and password to an access control system | ~ to one’s computer/account/network; login (n): type the ~; a ~ command file; log (n): keep a ~ of sth; a logbook (n); ant. log off/out | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | Password (n) | a secret word or phrase used to gain admission to a place; a string of characters that allows access to a computer, interface, or system | type/enter/change/require/supply/ know/forget the ~; ~ protection; be protected by a ~; a(n) (in)valid ~ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | Penetrate (v) | go into or through sth especially with force or effort; gain unauthorized access to sensitive data by circumventing a system's protections | ~ the market/into a system/sb’s words; penetration(n): high/deep ~; ~ level; (im)penetrable (adj): ~ barrier/network;syn. infiltrate, invade | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 | Privacy (n) | the state of being free from public attention; the right of a personto determine the degree to which s/he will share information about him/herself with others | loss/guarantee of ~; invade/protect ~; ~ concerns/issues/policy/setting; for ~ reasons/considerations/ protection; private (adj): a ~ network syn: confidentiality ant. publicity, public | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30 | Proprietary (adj) | sth owned by an individual or a company, which needs to be licensed from the owner before it can be used | ~ information/brand/rights/interests/ name /OS/database/software/ system/features; proprietorship (n); ant. open, public/generic (brand) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31 | Rely (v) | depend on sb/sth with full trust or confidence | ~ on/upon sb/sth; (un)reliable (adj), (un)reliability (n); syn. be confident of; depend on, trust | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | Risk (n) | exposure to danger, the possibility that something unpleasant or unwelcome will happen | ~-averse/aversion; the ~ factor; pose a ~; run/take the ~ of; a security ~; a ~ to safety; ~taker;risky (adj), riskiness (n);syn. insecurity, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33 | Safety (n) | the condition of being protected from or unlikely to cause danger, risk, or injury | cyber/public ~ ; assure/jeopardize sb’s ~; ~ barriers/precautions; safe (adj): stay ~ on the Internet, be ~ for sb/from sth; safely (adv); syn. security ant. insecurity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 34 | Scan (v) | look quickly but not very thoroughly through sth; convert a document or picture into digital form; check manually or automatically for viruses and malware | ~ for/through/into the computer; ~ data/information/library/the contents/pages/headings; scan (n): a quick ~ of sth; scanner (n): optical/ultrasound/colour/ desktop ~; buy/test/run the ~ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 35 | Secret (n) | not known or seen or not meant to be known or seen by others | guard/keep/divulge a ~; a(n) open/state/commercial/military ~; meet in ~; secretive (adj): be ~ about sth syn. cryptic, confidential, classified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 36 | Secure (adj) | protected against attack or other criminal activity | ~ connection/transaction; ~ against/from sth; security (n) : ~ policy/update/ environment/mechanism/service/ protocol/level; social/data ~; ensure/ compromise/undermine ~; ant. insecure, insecurity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 37 | Sensitive (adj) | quick to detect or respond to slight changes, signals, or influences; kept secret or with restrictions on disclosure to avoid endangering security | ~ to criticism/other people’s feelings/about sth; ~ information/issue/test/equipment/area; sense (n), (in)sensitivity (n); ant. insensitive | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 38 | Threat (n) | a person or thing likely to cause damage or danger, a potential for violation of security or inflicting harm | pose/constitute/cause/carry out/fulfill/face a ~; security/major/hidden ~; a ~ to public safety; under the ~ of sth; threaten (v), threatening (adj);syn. jeopardy, menace | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 39 | Valid (adj) | legally or officially acceptable or binding; in legal force | ~ contract/license/password/visa; (in)validity (n), (in)validate (v), (in)validation (n); syn. effective ant. invalid, ineffective | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40 | Vulnerability | a flaw or weakness in a system that could be exploited to violate the system's security policy | degree of ~; exploit/identify/fix a ~ on a system; in/vulnerable (adj): ~ group/position/to criticism; emotionally/feel ~; ant. immune, immunity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ACTIVITIES
Activity 1. Give synonyms:
| 1. authenticate | |
| 2. authorize | |
| 3. compromise | |
| 4. deny | |
| 5. endanger | |
| 6. disrupt | |
| 7. intrude |
Activity 2. Give antonyms:
| 1. encrypt | |
| 2. code | |
| 3. admit | |
| 4. vulnerable | |
| 5. confidential | |
| 6. succeed | |
| 7. cipher | |
| 8. proprietary |
Activity 3. Word family. Fill in the missing words of the same root where possible:
| Noun | Verb | Adjective | Adverb |
| confide | |||
| undeniably | |||
| validity | |||
| safe | |||
| detect | |||
| digital | |||
| penetration |
Activity 4. Complete the tables with words that form strong partnerships with the target vocabulary units:
| Verb | Target vocabulary unit |
|
a certificate | |
| Verb | Target vocabulary unit |
|
a firewall | |
| Target vocabulary unit | Noun |
|
confidential | |
| Target vocabulary unit | Noun |
|
code | |
| Target vocabulary unit | Noun |
|
dedicated | |
| Target vocabulary unit | Noun |
|
deny | |
Activity 5. Match the given terms with their definitions:
| 1. back door | A. disclose confidential information |
| 2. divulge | B. a feature or defect of a computer system that allows secret unauthorized access to data |
| 3. deny | C. sth categorized as officially secret, access to which requires authorization |
| 4. classified | D. internal consistency or lack of corruption in electronic data |
| 5. integrity | E. refuse to admit the truth or existence of sth |
| 6. threat | F. owned by an individual or a company, which needs to be licensed from the owner before it can be used |
| 7. proprietary | G. a person or thing likely to cause damage or danger |
Activity 6. Insert prepositions:
1. I have never come ___ such an aggressive attack before.
2. Medicines should not be used ___ expiry.
3. Travelling abroad one gets exposed ___ various cultures.
4. These efforts are doomed ___ failure.
5. The disc has not been checked ___ integrity.
6. I would hate to intrude ___ his privacy.
7. She didn’t post the information ___ privacy reasons.
8. You can surely rely ___ me.
9. Could you scan the document ___ the computer?
Activity 7. State the type of logical relations between the following concepts:
| Concepts | Logical relationship |
| 1. authorize-authenticate | A. general and specific |
| 2. firewall – security | B. cause and effect |
| 3. deny – admit | C. contrast |
| 4. scan – digitize | D. method and purpose |
| 5. character – password | E. part and whole |
| 6. filter - firewall | F. equivalence |
| 7. integrity – corruption |
Activity 8. Decode Bruce Schneier’s saying about computer security and comment on it:
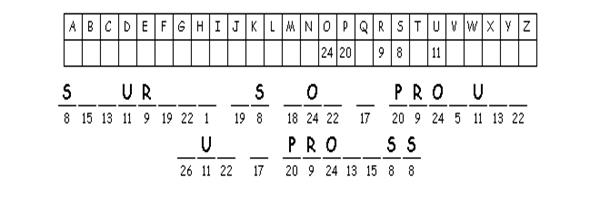
http://puzzlemaker.discoveryeducation.com/code/BuildCryptogram.asp
Activity 9. Explain the difference between the following concepts using the Venn diagram below:
| 1. disclosing – divulging information |
| 2. certificate – license |
| 3. confidential – classified information |
| 4. password – login – pin code |
| 5. data integrity – academic integrity |
| 6. safety – security |

Activity 10. Say what/who can be… and how:
| 1. secured | |
| 2. corrupted | |
| 3. certified | |
| 4. dedicated | |
| 5. in/validated |
Activity 11. Say what the following is used/done for:
| 1. authentification | |
| 2. authorization | |
| 3. encryption | |
| 4. back door | |
| 5. invalidation | |
| 6. coding | |
| 7. fail-safe mode |
Activity 12. Analyze the reliability of a) passwords; b) firewalls c) licenses.
Activity 13. Do a mini-research and enumerate the computer security measures a) on the part of the user b) on the part of a programmer. Evaluate their reliability.
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2019-04-19; Просмотров: 912; Нарушение авторского права страницы