Networks and Telecommunications
- What is the World Wide Web?
- technologies that provide access to information through telecommunications
- a collection of interconnected documents and other resources
- the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes
- global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities
- exchange of information over significant distances by electronic means
- What was the purpose of ARPANET?
- to develop a platform for the WWW
- to share research information
- an experiment to test sharing resources
- a university project to share MP3 files
- a super-secret government project to share classified data
- What is NOT true of a network?
- A network is a way to get “stuff” between 2 or more “things”
- Networks usually do not have internal connections
- A network allows sharing information among computer
- The postal system is an example of a network
- Metros are an example of a network
- How many devices are required for a network to be called a computer network?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- What is the scale of a PAN?
- Vicinity (e.g., Bluetooth)
- Building (WiFi, Ethernet)
- City (DSL)
- Country (Large ISP)
- Global
- What is the scale of a LAN?
- Vicinity (e.g., Bluetooth)
- Building (WiFi, Ethernet)
- City (DSL)
- Country (Large ISP)
- Global
- What is the scale of a MAN?
- Vicinity (e.g., Bluetooth)
- Building (WiFi, Ethernet)
- City (DSL)
- Country (Large ISP)
- Global
- What is the scale of a WAN?
- Vicinity (e.g., Bluetooth)
- Building (WiFi, Ethernet)
- City (DSL)
- Country (Large ISP)
- Global
- What type of connection do these networks represent?
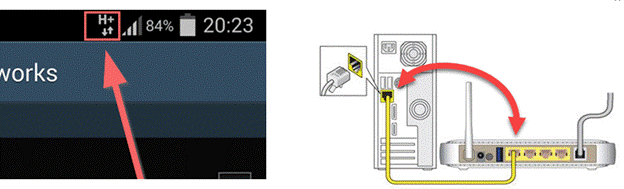 - Physical
- Virtual
- Intermittent
- Constant
- Logical
- What type of connection does this network represent?
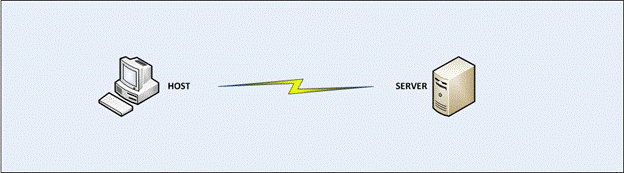 - Physical
- Virtual
- Intermittent
- Constant
- Logical
- What is the most common type of network topology used today?
- Fish
- Star
- Bus
- Ring
- Tree
- A laptop, smartphone, or server are examples of what network component?
- applications
- hosts
- routers
- links
- interfaces
- A DSL modem and wireless access points are examples of what network component?
- applications
- hosts
- routers
- links
- interfaces
- Wires, cables and radio signals are examples of what network component?
- applications
- hosts
- routers
- links
- interfaces
- Network-application and network-network are examples of what on a network?
- applications
- hosts
- routers
- links
- interfaces
- What is the function of the data layer?
- Transmit data by an electric voltage, radio frequencies, or light over a physical medium
- Sends data node-to-node
- Provides network addressing and routing (host-to-host)
- Delivers data from process-to-process
- Provides application services to users and programs
- What is the function of the network layer?
- Transmit data by an electric voltage, radio frequencies, or light over a physical medium
- Sends data node-to-node
- Provides network addressing and routing (host-to-host)
- Delivers data from process-to-process
- Provides application services to users and programs
- What is the function of the transport layer?
- Transmit data by an electric voltage, radio frequencies, or light over a physical medium
- Sends data node-to-node
- Provides network addressing and routing (host-to-host)
- Delivers data from process-to-process
- Provides application services to users and programs
Cybersecurity
- Cybercrime refers to anything done with criminal intent using ______.
- A smartphone
- The internet
- A computer
- An internet connected device
- A computer connected to the internet
- What do hackers and cybercriminals do for a living?
- Work regular jobs and hack on the weekends
- Are plumbers or electricians with nothing better to do
- Hack and steal for a living
- Unemployed people with IT skills just trying to put food on the table as they look for a job
- Steal from the rich to give to the poor
- What describes the cybercrimes category of “Computer as a Tool”?
- Using a computer to target an individual
- Targeting a computer or system to commit a crime
- Using a computer to sell illegal goods
- Hate speech or Harassing someone through cyberspace
- none of the above
- What describes the cybercrimes category of “Computer as a Target”?
- Using a computer to target an individual
- Targeting a computer or system to commit a crime
- Using a computer to sell illegal goods
- Hate speech or Harassing someone through cyberspace
- What describes the cybercrimes category of “Selling Illicit Goods”?
- Using a computer to target an individual
- Targeting a computer or system to commit a crime
- Using a computer to sell illegal goods
- Hate speech or Harassing someone through cyberspace
- none of the above
- What describes the cybercrimes category of “Offensive Content or harassment”?
- Using a computer to target an individual
- Targeting a computer or system to commit a crime
- Using a computer to sell illicit goods
- Hate speech or online stalking
- none of the above
- Spam, phishing scams, and identity theft are examples of which type of cybercrime.
- Computer as a Tool
- Computer as the Target
- Selling Illicit Goods
- Offensive content or Harassment
- none of the above
- What does malware stand for?
- nothing special, just malware
- malfunctioning software
- malicious software
- malfunctioning hardware
- malice-ware
- What is not a risk of pirated software?
- likely contains malware
- a cybercriminal can use your computer to commit cyber crimes
- might contain undetected keylogging software
- none of the above are risks
- All are risks of using pirated software
- How does malware infect your computer?
- untrusted websites
- email attachments
- pirated software
- infected flash drives
- all of the above
- This list contains a passphrases and passwords. Which is the passphrase?
- I want 2 smile more: )
- (? fFeT! I#7TVJK?
- gDR4qLEB7g
- KN%6hGYgEqdVvAt7#W
- sd3WPYJZCs
- What do difficult targets do?
- Use weak passwords
- Use Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Respond to spam
- Click links in emails
- Visit shady internet sites
- Run pirated software
- What do easy targets do?
- Are security conscious
- Understand the dangers and risks
- Use encryption
- Click links in emails
- Use strong passwords
Internet Technologies
- What is the most common form of network architecture on the internet?
- Peer-to-peer
- Client-server
- Ring
- Bus
- Tree
- Typically, how do clients and servers interact?
- One-to-one (one client to one server)
- One-to-many (one client to many servers)
- Many-to-one (many clients to one server)
- Many-to-many (many clients to many servers)
- None of these. Clients and servers do not interact
- The unique name of a computer on the internet
- IP address
- ISP
- domain name
- URL
- Web hoster
- The unique address of a computer on a network
- IP address
- ISP
- domain name
- URL
- Web hoster
- The exact location of a document on the web
- IP address
- ISP
- domain name
- URL
- Web hoster
- Connect websites to the internet
- IP address
- ISP
- domain name
- URL
- Web hoster
- A software program which interprets the HTML documents and displays it on the user’s screen
- web browser
- web hosting provider
- internet service provider (ISP)
- domain registrar
- domain name system (DNS)
- Connects clients to the internet
- web browser
- web hosting provider
- internet service provider (ISP)
- domain registrar
- domain name system (DNS)
- Maps the domain name to an IP address
- web browser
- web hosting provider
- internet service provider (ISP)
- domain registrar
- domain name system (DNS)
- What is an example of a TLD (top level domain)?
Study hint: identify the rest of the answers. - 212.87.38.45
- do.ektu.kz
- https: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPv6_address
- index.html
- .com
- An IPv6 address uses what format?
- Binary (base 2): 11001100.10000100.00101000.10011011
- Octal (base 8): 0300.0250.0057.0352
- Decimal (base 10): 192.168.1.82
- Hexadecimal (base 16): 2001: db8: a0b: 12f0:: 1
- none of the above
- What service allow users to acquire domain names?
- ISP
- DNS
- Domain registrar
- Web hoster
- None of these
- What protocol do the web browser and web service use?
- FTP
- UDP
- NTP
- HTTP
- IP
- Why is TCP/IP such an important web protocol?
- It’s fast. It makes sure the data arrives as quickly as possible
- It’s secure. It makes sure that hackers cannot see the data en route
- It guarantees delivery. It guarantees that data arrives intact, which creates a duplicate of the original file
- It reduces redundancy. It doesn’t care if data is lost, such as when streaming a movie.
- It’s efficient. It uses less resources than UDP.
- How does TCP handle lost data or packets during transit?
- TCP must initiate a new connection with the server
- TCP must stop the file transfer and then restart at the beginning of the file
- TCP knows what packet was lost. So, it will request only the lost packet.
- TCP is smart enough to know if the packet is important (maybe the file doesn’t need the data)
- Data packets never go missing.
- What is the role of IP in the TCP/IP internet protocol stack?
- Creates a virtual connection
- Carries the data to the final destination
- Splits the data into small packets
- Guarantees data delivery
- Reassembles the data to create a replica of the file
- Defines the presentation and style of the web page.
- HTML
- CSS
- Python
- JavaScript
- Ruby
- Controls the behavior of the web page.
- HTML
- CSS
- Python
- JavaScript
- Ruby
- In HTML, what is text that links to other information, or to other web pages? (what does the H stand for).
Study hint: What does HTML stand for? - hypertext
- hyper-extensions
- markup
- language
- hypermedia
- In HTML, what are links on a web page called?
- hyper-extensions
- hyperlinks
- markup
- language
- hypermedia
- Which is JavaScript?
Study hint: identify the rest of the answers. - < i> This text is italics< /i>
- h1 { color: orange; }
- for (i = 0; i < cars.length; i++)
- < p> The price of < i> rice< /i> today is 459 won.< /p>
- p { font-size: 20px; }
|

