
|
Архитектура Аудит Военная наука Иностранные языки Медицина Металлургия Метрология Образование Политология Производство Психология Стандартизация Технологии |

|
Архитектура Аудит Военная наука Иностранные языки Медицина Металлургия Метрология Образование Политология Производство Психология Стандартизация Технологии |
Change in the magnitude of demand
Non-price factors of demand cause a change in demand itself. At the same time, the demand curve moves to the right or to the left, depending on the content of the factors themselves. Increase in demand shifts the demand curve to the right and up, and a decrease in the demand value shifts the demand curve to the left downwards.
2. Offer of an individual enterprise.The law of supply Concept of the supply If the demand for the goods arises from the consumers, then the offer comes from the producer of the products. Supply can be defined as the ability of enterprises (organizations) to sell products on the market for certain prices. • Value of the supply - the volume of products that the domestic producers are ready to sell for a certain time on the market at an appropriate price.
The law of supply Supply of producers are related with many factors in the market, but the main one is the price. Therefore, the relationship between the volume of supply of products on the market and its price is directly dependent. This dependence has regularities. • Law of the supply says: with the increase in prices, the quantity of supply increases, and with the decrease in prices, the supply of goods is reduced. Supply law shows that producers are ready to manufacture and offer to the realization of a greater quantity of its product at a higher price than they would like this is done at a lower price. This is because the price of the product depends on the revenue of the manufacturer. In turn, revenue determines the profit margin /размер прибыли/ of the organization. High revenue corresponds - is usually greater profits. In addition, it is necessary to note that a low price may not cover the cost of production and sale of products. Therefore, it is the price of the goods that is the main material stimulus of the enterprise.
Supply curve A direct relationship between the amount of supply and the price of the product can be depicted graphically: this results in an upward direction of supply curve (Graph 6.3).
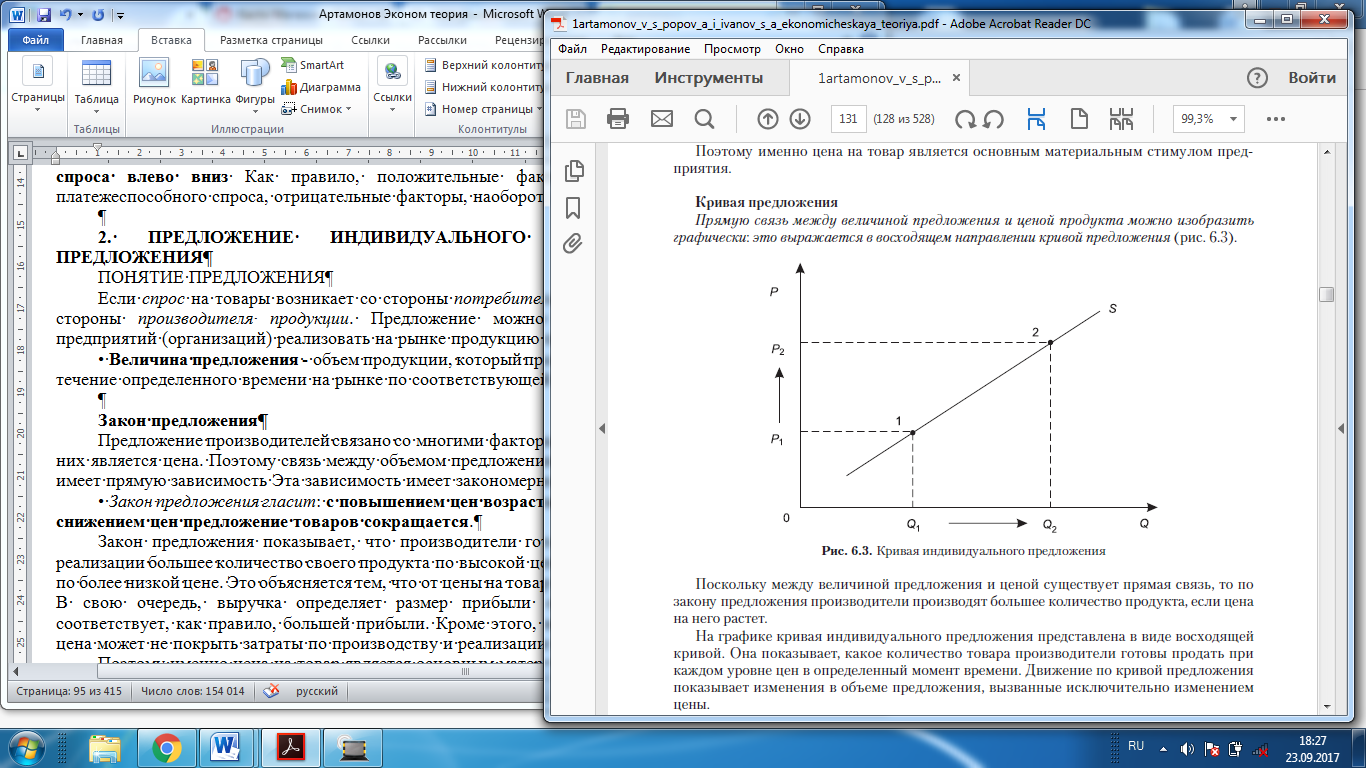 Since there is a direct relationship between the value of the supply and the price, to the law of supply, producers produce more product if the price it grows. Since there is a direct relationship between the value of the supply and the price, to the law of supply, producers produce more product if the price it grows.
On the graph, the curve of the individual supply is presented in the form of an ascending curve. It shows how many products producers are willing to sell at each level of prices at a certain point in time. Motion along the supply curve shows the changes in the volume of supply caused solely by the change prices. Non-price factors of supply The theory and practice show that to value of the producer's proposal, besides price factors, is influenced by non-price factors. This is due, above all, to those conditions that directly affect to the production scale (increase or decrease of volume of production of at preservation of prices). Non-price factors have an positive or negative impact on producer (Table 6.2).
Table 6.2 - Non-price factors of supply
Thus, non-price factors cause changes in supply, which is displayed by a corresponding shift in the supply curve (Figure 6.4).
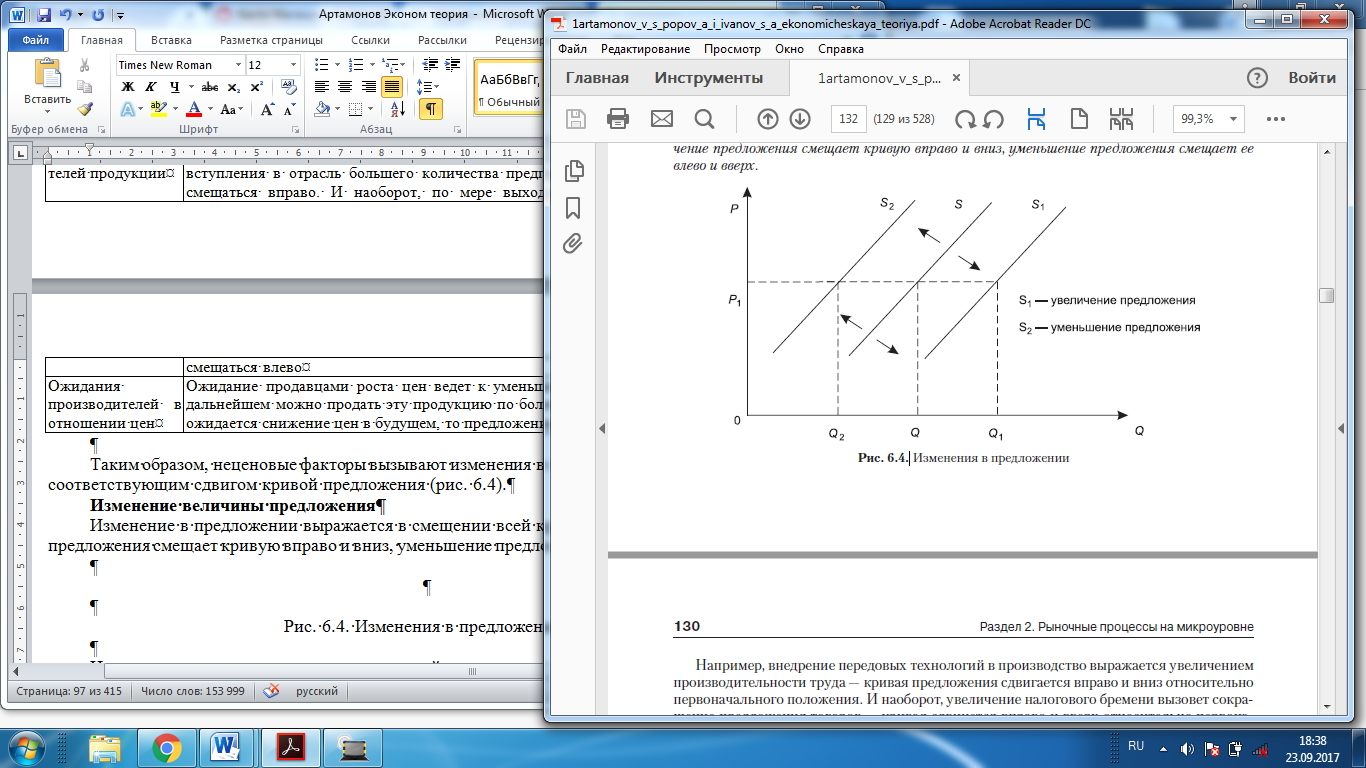
The change in supply is expressed in the displacement of the entire supply curve: increase of supply shifts the curve to the right and down, a decrease in the sentence shifts it left and up. For example, implemented of advanced technologies in production reflected the increase of labor productivity - supply curve shifts to the right and down relative initially position. Conversely, an increase in the tax burden will cause a reduction in the supply of goods - the curve will move to the right and upward relative to the initial position. At the same time, the price of the product will increase, and the supply volume will decrease.
3. Equilibrium of supply and demand.The equilibrium price Having ascertained the laws of supply and demand, it is necessary to consider the mechanism of market equilibrium. In order to understand how the market determines the price of a product and its quantity, which is actually sold and bought, it is necessary to analyze the mechanism of interaction between supply and demand.
► Market equilibrium is a state of the market in which demand for goods coincides with its supply, and business entities are not interested in changing it. Market equilibrium is characterized by an equilibrium volume and an equilibrium price ► The equilibrium price is the price at which demand is equal to supply, and under these conditions there is no tendency to change it. ► The equilibrium volume is the volume of demand and supply, which corresponds to the equilibrium price. The ability of supply and demand to set a price at the level at which decisions about the sale and purchase are synchronized, is called the balancing price function. The equilibrium price unloads the market without leaving onerous surpluses for the sellers and without creating appreciable shortages for potential buyers. If these competitive prices did not automatically agree with each other on the supply and demand decisions, some kind of administrative control from outside governments to eliminate and manage shortages and excesses that otherwise case could arise. Market equilibrium exists as a result of a pervasive disruption and a restoration of the balance between supply and demand. In essence, this equilibrium is dynamic. ► Stability of equilibrium is the ability of a market system to restore market equilibrium in the face of internal forces or factors. At a price P1 above the equilibrium supply is more demand, and the market appears surplus. Surplus - this is a state of the market when the supply is more demand, and market the price is above the equilibrium price. In these circumstances, there is competition between producers, which stimulates price reductions. The supply of goods decreases, and demand, on the contrary, increases. The market is moving towards establishing equilibrium. At a price P2 below the equilibrium demand is more than supply, and there is a deficit in the market. Deficiency - this is a state of the market in which demand is greater than supply, and the market price is below the equilibrium price. In this case there is a competition of buyers who are already ready to pay a high price for this product. In these conditions, supply of producers is growing, and demand is gradually decreasing. Market system again moving in the direction of establishing equilibrium. It should be noted that in a competitive environment, the imbalance in market equilibrium and the deviation of the market price from equilibrium can’t be long, since equal weight, in principle, is established on the basis of the mechanism of self-regulation.
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2019-04-19; Просмотров: 284; Нарушение авторского права страницы