
|
Архитектура Аудит Военная наука Иностранные языки Медицина Металлургия Метрология Образование Политология Производство Психология Стандартизация Технологии |

|
Архитектура Аудит Военная наука Иностранные языки Медицина Металлургия Метрология Образование Политология Производство Психология Стандартизация Технологии |
Method of point elasticity
This method is used if there is functional relation consideration factors and should evaluate their mutual sensitivity in corresponding point. This relationship characterizes the relative change of one factor (for example, the volume of demand) with an infinitesimal change of another factor (for example, price): E = Q' (P) where: Е - coefficient of elasticity; Q'(P) is the derivative function of demand (or supply) at a price; P - market price; Q(P) - the amount of demand (or supply) at a given price. Let’s consider the following example: Estimation of point elasticity Let a function of demand for potato has the form Q d = 4.000 - 25P. Let’s estimate the elasticity of demand for the price of this product, if the market price was P = 10 monetary units per kg. To calculate the elasticity coefficient E, it is necessary to know the volume of demand at the existing price Q(P) and the derivative of the demand function at the price Q'(P). With a price of P = 10 monetary units per kg. Q d = 4000 - 25 P = 4000 - 25 × 10 = 3750 monetary units. Q'(P) = - 25. Substitute the obtained values in the formula: E = Q'(P) The economic sense of the received coefficient is the increase of potato prices by 1% relatively to the initial level will lead to a reduction in the demand value of 0,066%. The value of the received coefficient give evidence of a low elasticity of demand for the product in question. This method is characterized by high precision of results. At the same time, the need to make significant expenditures for preliminary market research and the derivation of the actual demand function for the factors of interest makes this method very expensive .
Method of arc elasticity This method is used in the case when practical observations do not allow us to determine the functional relation between the indicators interest to us. In such conditions, the market reaction is evaluated in the transition from one state (one point) to another state (another point), for example, a change in sales with an increase in price. Elasticity determination between two points on the demand or supply curve supposes knowledge of the initial and subsequent levels of the studied parameters, for example, prices and volumes. However, during calculations it is necessary to use the average values of the indicators: E = where: Р1 , Р2 - initial and subsequent prices; Q1, Q2 - initial and subsequent demand. Estimation of arc elasticity In purpose to stimulate sales, the company announced a decrease in prices for its products from 24 to 18 money units per unit. As a result, the enterprise increased sales volume from 10,000 to 18,000 units of product. Calculate the elasticity of consumer demand by the method of arc elasticity: E = Conclusion: the economic meaning of the coefficient lies in the fact that a decrease in the unit price by 1% leads to an increase in demand of 2%, which indicates a high elasticity of demand for the price of this product. Using this method gives an approximate value of the elasticity coefficient, the elasticity of demand. The degree of price elasticity or inelasticity of demand is measured using the coefficient of price elasticity, which is determined by the formula:
Elasticity of demand for income = In addition to the price factor, the consumer's income also affects the change in the market situation. Therefore, in addition to the elasticity of demand and price, it is possible to determine the elasticity of demand for income. The coefficient of elasticity of demand always has a negative value because demand and price change in opposite directions. However, for simplicity of analysis, it is considered as a positive quantity. In economic theory, the following types of price elasticity of demand are considered: • elastic demand: when the price decreases, the number of sales sharply increases and the total revenue increases; • unitary elasticity: the price reduction is compensated by the growth of sales, and the total revenue remains unchanged. For example, a one percent price reduction causes a one-percent increase in sales; • inelastic demand: the price decrease slightly changes the sales volume, the total you handle is reduced; • perfectly elastic demand: the price of the product does not change, despite the change in demand; • perfectly inelastic demand: a change in price does not have any effect on the volume of demand at all.
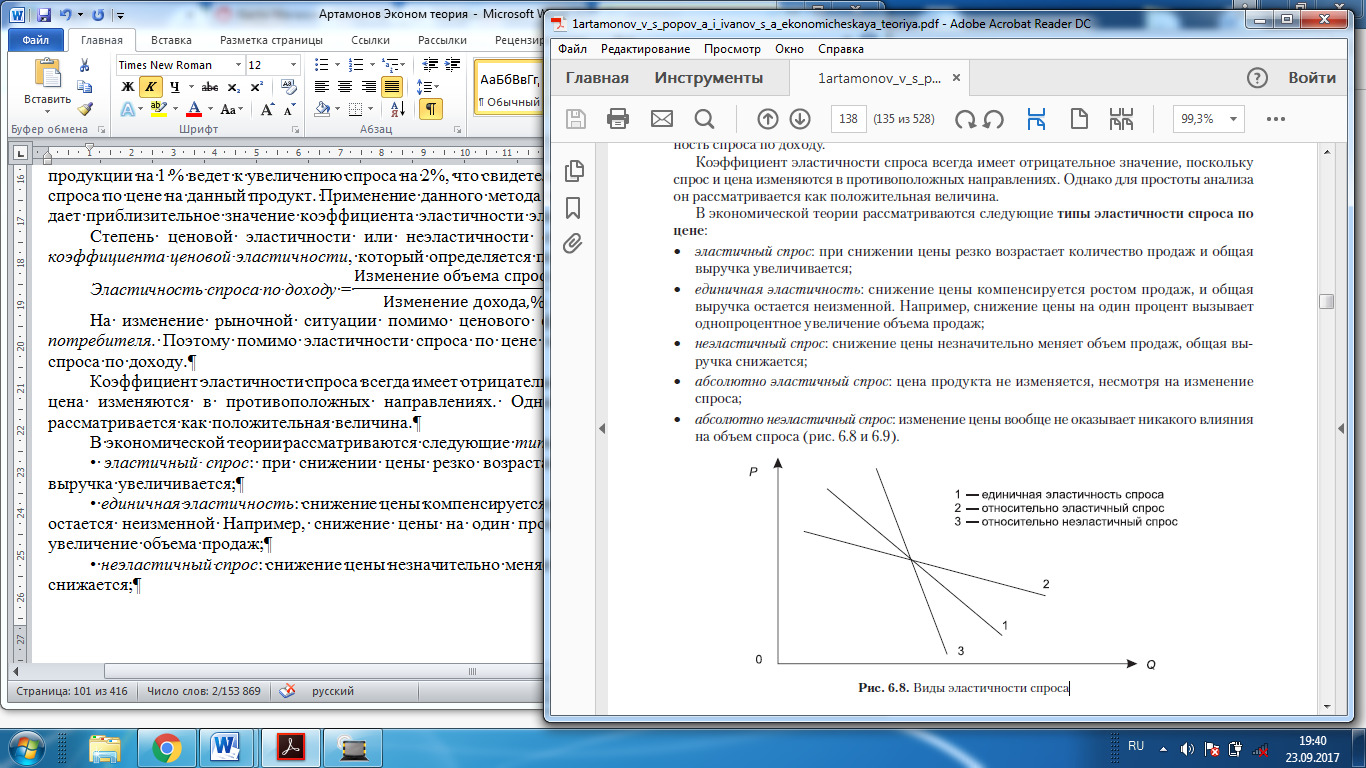
Graph 6.8 - Types of elasticity of demand Graph 6.9 - Extreme cases of elasticity of demand
The elasticity of demand is influenced by certain factors (Table 6.3).
Table 6.3 - Factors affecting the elasticity of demand
Elasticity of supply The degree of change in the volume of supply, depending on the increase in price, makes the supply elastic. It is measured by the elasticity of supply and is calculated by the same formula as the coefficient of price elasticity of demand. The only difference is that instead of the amount of demand, the value of the offer is taken. The offer is inelastic if the price change does not cause a change in the offer. The offer is considered absolutely elastic, when the slightest reduction in the price of the goods causes the supply to decrease to zero, and the slightest increase in the price causes an increase in supply In economic theory, consider the following guides types of elasticity of supply for the price: • elastic supply: means high sensitivity to the price at which the elasticity index is more than 1; • supply of unitary elasticity: means the same degree of change in price and volume of production; • inelastic supply: means a lower sensitivity to the price at which the elasticity index is less than 1; • perfectly elastic supply: any quantity of the goods will be offered at a fixed price; • perfectly inelastic proposal: a change in price does not have any effect on the supply volume at all. The proposal, since it is associated with a change in the production process, is slower to adapt to price changes than demand. Therefore, the time factor is the most important in determining the elasticity index. Usually, when assessing elasticity, three time periods are considered: short-term, medium-term and long-term (Table 6.4).
Table 6.4 - Time factor affecting to supply elasticity
5. Price: concept and essence. Classification of prices |
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2019-04-19; Просмотров: 280; Нарушение авторского права страницы