Description of the work of team members
The table represented below (table 2) demonstrates the list of team members and their key responsibilities at the different project stages.
Table 2. Distribution of tasks
| №
| Name
| Stage 1 «Initiation»
| Stage 2
«Planning»
| Stage 3 «Assemb-
ling»
| Stage 4 «Program-
ming»
| Stage 5 «Closing»
|
| 1
| Gintciak Aleksei
| Brainstorming, organization of meetings, communication with L.Chechurin
| Planning, math and Simulink modeling,
writing of business plan
| Assembling
| Writing of program code
| Participation in writing of final report
|
| 2
| Pridanova Ekaterina
| Brainstorming, writing of patent
| Planning, writing description of math and Simulink models, writing of business plan
| Assembling, returning of components
| \Writing of program code
| Final report correction, translation
|
| 3
| Lisovodskaya Ksenia
| Assessment of the implementation of ideas, brainstorming, organization of meetings
| Planning, development of composition of details, financial planning for purchasing, writing of business plan
| Participation in assembling, purchasing of details
| Participation in assembling, program code consulting
| Participation in final report writing, reviewing
|
| 4
| Shapovalov Roman
| Organization of brainstorming
| Planning, develop-
ment of composition of details, creation of drawings in SolidWorks, writing of business plan
| Participation in assembling
| Participation in assembling, searching of referent links
| Participation in final report writing
|
| 5
| Shklyarova Darya
| Brainstorming, logging
| Planning, timeline planning
writing of business plan
| Participation in assembling
| Participation in assembling, searching of referent links
| Video recording and montage
|
| 6
| Tsolan Dmitry
| Brainstorming
| Planning, financial planning for purchasing writing of business plan, development of composition of details
| Participation in assembling, purchasing of details
| Participation in assembling, searching of referent links
| Participation in final report writing
|
Budget
The purchasing list and list of returned detail are represented in the table 3.
Table 3. List of bought and returned components
| Bought
|
| Returned
|
| №
| Description
| Pts
| Price
| Total
|
| №
| Description
| Pts
| Price
| Total
|
| 1.
| Power 9V to 2.1mm Barrel Jack
| 4
| 30
| 120
|
| 1.
| AA battery Superlife 1.5 V
| 3
| 78
| 234
|
| 2.
| M/F 40 Pin Jumper Wire
| 1
| 350
| 350
|
| 2.
| Bluetooth Module BK3231 without pins
| 4
| 180
| 720
|
| 3.
| 9V Battery Snap
| 4
| 9
| 36
|
| 3.
| Battery Holder AA*4
| 4
| 28
| 112
|
| 4.
| 9V Alkaline Battery
| 7
| 180
| 1260
|
| 4.
| Point Interlocking Solderless Breadboard
| 2
| 180
| 360
|
| 5.
| Electrical tape
| 1
| 80
| 80
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 6.
| Shrink wrap 1 m
| 2
| 26
| 52
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 7.
| AA battery Superlife 1.5 V
| 4
| 78
| 312
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 8.
| Ultrasonic Sensor HC-SR04
| 4
| 90
| 360
|
|
| 5816
|
|
|
|
| 9.
| Bluetooth Module BK3231 without pins
| 4
| 180
| 720
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.
| Laser module KY-008
| 1
| 40
| 40
|
|
| Inventory:
|
|
|
|
| 11.
| M/M 10 Pin Jumper Wire
| 1
| 50
| 50
|
|
| 1184
|
|
|
|
| 12.
| SERVO MOTOR SG90
| 2
| 120
| 240
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 13.
| Arduino UNO + micro-USB
| 3
| 350
| 1050
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 14.
| F/F 10 Pin Jumper Wire
| 1
| 60
| 60
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 15.
| Bluetooth Module BK3231
| 4
| 200
| 800
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 16.
| Point Interlocking Solderless Breadboard
| 2
| 180
| 360
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 17.
| Glue
| 1
| 28
| 28
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 18.
| Сonstructor "Helicopter"
| 1
| 162
| 162
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 19.
| Battery Holder AA*4
| 4
| 28
| 112
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 20.
| Bluetooth-module HC-05
| 1
| 320
| 320
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 21.
| Radio-module NRF24L01+
| 9
| 70
| 630
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Project risks
The following risks were identified, which may affect the completion of the project:
1. Low quality of details
2. Unattainability of the product's functional characteristics
3. Lack of knowledges
4. Low activity of team members
5. Use of funds beyond the budget
6. Lack of time
7. Extreme value fluctuations of currencies exchange rate
8. Lack of necessary details in the shop
9. Lack of cat
After that arrange it in the matrix of risks considering probability of their occurrence and influence on our project (table 4).
Table 4. Matrix of risks
| Influence on
project
| Probability of occurrence
|
| Low
| Medium
| High
|
| Low
|
|
|
|
| Medium
| 5,7
| 6
| 3
|
| High
| 4,8,9
| 2
| 1
|
Descriptions of colors:
|
| Low level of risk
|
|
| Medium level of risk
|
|
| High level of risk
|
|
| Extreme level of risk
|
We decided to manage only those risks that could seriously impact on the project implementation (high and extreme level). The result you can see in the table 5.
Table 5. Methods of risk management.
| Description of risk
| Efforts to minimize the risk
| Achieved?
|
| Low quality of details
| Acceptance of risk
| ✔
|
| Unattainability of the product's functional characteristics
| Consultation with an Arduino experts
| ✖
|
| Lack of knowledges
| Consultation with an Arduino experts
| ✔
|
| Low activity of team members
| Motivational speech of Roman with denotation of place where we are and where we will be on exam
| ✖
|
| Lack of time
| Careful planning of activity
| ✖
|
| Lack of necessary details in the shop
| Monitoring of prices in different shops
| ✔
|
| Lack of cat
| Acceptance with preparation of cat’s costume
| ✔
|
Project perspectives
The realized principle of the device operation may be needed in other technological systems. For example:
● This device can be adapted to move animals (for example, tigers, lions and other dangerous cats) into the cage, it will reduce the risk of injury and protect working conditions of farm staff (zoos, circuses);
● Search for different stuff in the house (example: TV remote control, socks);
● Level correction (for example: when you determine the position of objects and correct their position in the construction using a laser level);
● Use as a simulator (example: training techniques of kicking in martial arts or instruction system of driving);
● Automate the lighting system (example: correction of the direction of the light ray during the performance of the actor in the theater) and so on...
In addition, you can use arduino Nano to reduce the size of the device on the cat or (and) change the principle of data transfer, in order to the system becomes more like a real-time system.
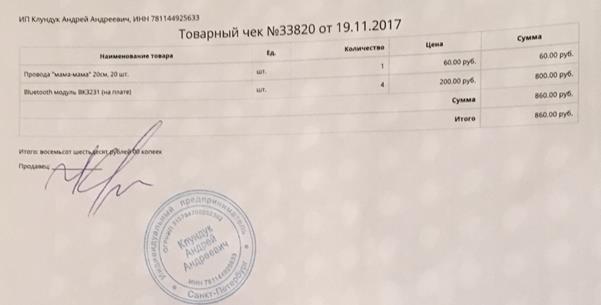
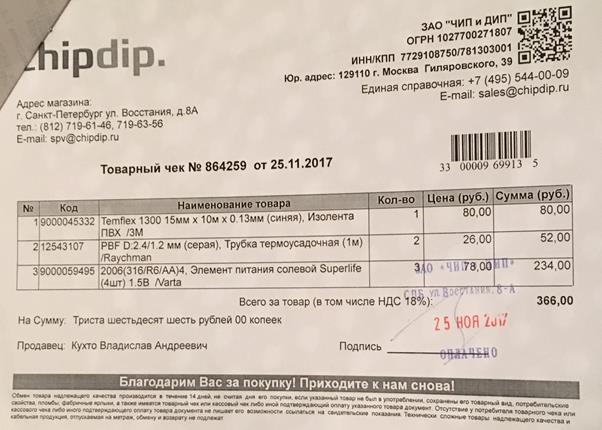
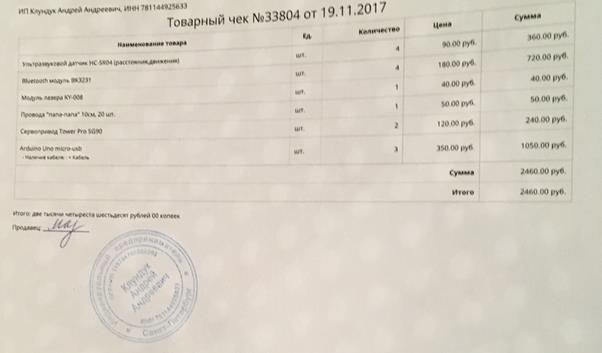
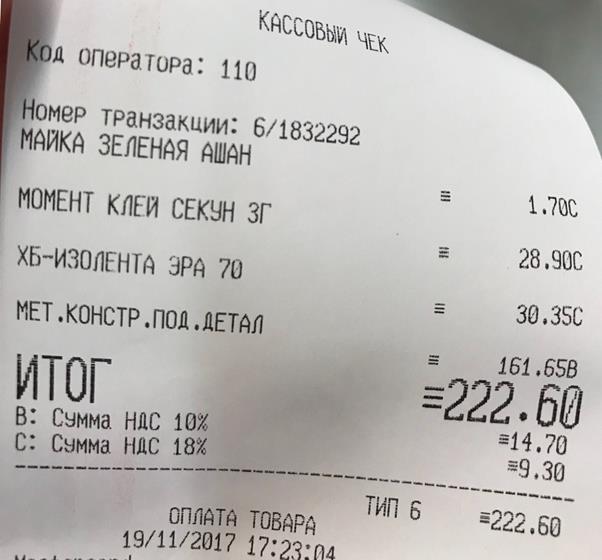
Appendix 1. Receipts